To learn about the basic of electronics we are here to help you as many ways as possible to understand the knowledge of electronics the very basic of electronics that what electronics really mean so collectpdf.blogspot.com not only provide you to the pdf of all relevant subject to understand the basic of those particular subjects but you can also grasp the really needy basics of all those subjects through collectallpdf.blogspot.com.
Firstly we have to understand what electronics really mean, which will help you in the future so that you are able to answer the very tiny basics of electronics.
Through collectallpdf.blogospt.com you can read also the very basic fundamentals of electronics which will help you to crack any technical interview of electronics related questions.
We are here to provide you all the important questions related to electronics which will help you to answers all questions during your interview here we provide all-important questions that are very common to ask in an interview which will be part of many technical rounds of an interview.
So, firstly we have to understand what is electronics what is the main parts of electronics what is the basics devices which will include in the electronics and so on so forth.
WHAT IS ELECTRONICS?
ELECTRONICS deals with the development and application of devices and systems involving the flow of electrons in a vacuum, gas and in semiconductors.
It is considered to be a branch of physics and electrical engineering. it also deals with the electrical circuits that involve active electrical components such as transistors, diodes, integrated circuits, sensors, and an associated passive electric component.
There are 2 types of electronic components:
1. PASSIVE COMPONENTS
2. ACTIVE COMPONENTS
PASSIVE COMPONENTS:
- Passive components are devices that store energy in the form of voltage or current.
- Or the components which can not control the flow of current.
- Passive components cannot provide any poor gain to the circuits.
- For example Resistors, Capacitors, Inductors Transformers.
ACTIVE COMPONENTS:
- Active elements generate energy in the form of voltage or current.
- They supply energy to the circuits and they can control the flow of current.
- Also, they can provide power gain to the circuit.
- For examople: Transistors, triode, Vaccume tubes , Voltage sources.
Now we have to understand the heart of electronics which we call a circuit, we will see different types of circuits such as electronic circuits, electrical circuits, analog circuits, and digital circuits, etc.
CIRCUIT
- Circuit can be electrical ,electronic, analog, digital synchronous ,asynchronous ,etc.
- Electrical circuit-A complete electrical network with a closed-loop giving a return path for current.
- Electronic circuits-it is a combination of electronic components capable of performing amplification, computation and data transfer.
- Anolg circuit uses continous and digital circuit uses discrete signal levels ,respectively.
TWO TYPES OF CIRCUITS ARE:
a) SERIES CIRCUIT
b) PARALLEL CIRCUIT
SERIES CIRCUIT
- Components are wired one after another.
- Electricity will pass through the first component, then the next component, then the next, and so on.
- In a series circuit, the current through each of the components is the same, and the voltage across the circuits is the sum of the voltages across each component.
PARALLEL CIRCUIT
- Components are wired side by side.
- Electricity passes through all of them at the same time, from one common point to another common point.
- In a parallel circuit, the voltage across each of the components is the same, and the total current is the sum of the currents through each component.
CLOSED CIRCUIT
- A complete electrical circuit through which current cam floe when a voltage is applied.
- A closed-circuit will allow the flow of electricity between power and ground.
- It is used when requiring the use of current.
OPEN CIRCUIT
- An incomplete electrical circuit in which no current flows.
- An open circuit will break the flow of electricity between power and ground.
these are the different types of circuits, as shown above, Now to understand the basic parameter of electronics we have to study about current and voltage because these are the essential parameter to learn electronics whole electronics is based on these parameters so let understand the different parameters.
CURRENT(I)
- Current is the movement or flow of electric charge.
- Or the continuous and uniform flow of charge around the circuit.
- According to Ohm's law, Current is given by I=V/R.
- Measured in units of 'Amperes'.
There are two types of current:
a) ALTERNATE CURRENT
b) DIRECT CURRENT
ALTERNATING CURRENT(AC)
- In AC the direction of electricity flowing throughout the circuit is constantly reversing.
- AC is obtained From Alternators.
- It can be transmitted over a long distance with some losses.
- For example Current flowing in power lines or Normal household electricity that comes from a wall outlet.
DIRECT CURRENT(DC)
- In DC the flow of electric charge is unidirectional.
- DC is obtained from generators, batteries, solar cells, etc.
- It can be transmitted over a long distance with negligible losses.
- Used to charge batteries, cell phones, flat-screen TVs (AC goes into the TV, which is converted to DC), Flashlight, etc.
VOLTAGE(V)
- Voltage is the difference in electric potential between two points.
- According to Ohm's law, voltage is given by V=I*R.
- Measured in units of 'VOLTS'.
we have completed all the basic parameters of electronics NEXT we will see all basic components related to electronics there are lots of electronic components but we study the important and basics component of electronics which are most commonly used in any electronic circuited we acquire knowledge of all the basic component through coolectallpdfblogspot.com now.
BASIC ELECTRONIC COMPONENT:
Here are some basic electronic components such as a resistor, diode, capacitor, inductor, transistor we will study all basic components through collectallpdf.com one by one.
RESISTOR(R):
- The resistor adds resistance to the circuit and reduces the flow of electrical current.
- If too much current through an LED, it is destroyed. So a resistor is used to limit the current.
- The different markings on the resistor represent different values of resistance.
- The values are read from left to right towards the gold band.
- The first two colors represent resistor's value.
- The third represents the multiplier.
- And the fourth(the gold band) represents the tolerance.

RESISTANCE
- Resistance is the opposition to the flow of current.
- Or measures of difficulty to pass an electric current through a conductor.
- According to Ohm's law, Resistance is given by R=V/I.
- It is measured in units of 'Ohms'.
- Conductors have very little resistance.
- Insulators have large amounts of resistance.
CAPACITOR
Capacitor stores potential energy in an electric field.
- The amount of electrical energy a capacitor can store is called capacitance.
- Capacitance is given by C=Q/V, where Q is a charge and V is a Voltage.
- Capacitors are measured in farad.
- The common capacitors are ceramic disk and electrolytic.
- Capacitors can smooth out a signal-eliminate the ripples or spikes in DC voltage.
- Capacitors are used in energy storage, Sensing, wattmeter, timing devices, etc.
INDUCTOR
- Inductor temporarily stores the electrical energy in the form of a magnetic field.
- It consists of a coil of copper wire.
- When the electric current is passed through the coil, the magnetic field is produced and stored in the coil of copper wires.
- It is used in filters, sensors, transformers, motors, etc.
- The transistor is a semiconductor device used to amplify or switch electrical signals and electrical power.
- Transistors have 3 pins: That is collector, emitter, and base.
- The basic type of transistors is PNP and NPN.
- PNP transistors allow electricity to pass from emitter to collector pin.
- NPN transistors allow electricity to pass from collector to emitter pin.
- Transistors are used as simple switches, voltage and power amplifiers, etc.
DIODES
- They allow electrical current to pass through them in only one direction.
- A diode has low resistance in one direction, and high resistance in other directions.
- Types of didodes are crystal diodes, gunn didodes, light emmiting diodes,Laser diodes,Zener diodes,Tunnel diode,PIN diode,photodiode etc.
- Diodes are used in radio demodulation, Power conservatuon, Logic gates , Temprature measurement, etc.
Now we discuss some important types of diodes so that it will help us to understand the basic differences among a different type of diode because all the diodes have different characters so that they differ by each other.
By collectallpdfblogsopt.com we can easily understand the common differences among all of the diodes.
- LED stands for Light-emitting diode.
- A special type of diode that lights up when electricity passes through it.
- Color o the light is determined by the energy bandgap of the semiconductors.
- LED's are used in automotive headlamps, advertising, traffic signals, camera flashes, etc.
- LEDs are widely used because of lower energy consumption, longer lifetime, smaller size and faster switching.
LASER
- LASER stands for light amplification by stimulated emission of radiation.
- It is the main cause of population inversion.
- When the charge concentration is more in higher energy level with respect to lower energy level it will be called as population inversion.
- This type of emission is called spontaneous emission.
- The laser diode is made up of direct bandgap material.
Another basic part of electronic circuitry is a switch, switches are of the different types to learn more about the types of switches firstly we have to understand what is meant by switches? how they work? functions of a different type of switches?
To clear understanding of all of these questions, you can go through collectallpdf.com which will definitely be helping you with your crystal clear concept about electronics.
So now we have to understand all about switches.
WHAT IS SWITCH?
SWITCH:
- A switch is an electrical component that can "make" or "break" an electrical circuit.
- The mechanism of a switch removes or restores the conducting path in a circuit when it is operated.
- Switches are the safest way to stop or start the flow of electricity in a device.
- An example of an electronic switch is a relay, analog switch, etc.
- Switches are used for on/off control. user input, etc.
Switches can be of:-
b)ELECTRONIC SWITCH
MECHANICAL SWITCHES:
- Mechanical switches must be activated physically by moving, pressing, releasing, or touching its contacts.
- The types of mechanical switches are
- Single pole single throw. single pole double throw, double pole single throw, double pole double throw, etc.
ELECTRONIC SWITCHES:
- Electronic switches do not require any physical contact in order to control a circuit.
- these are activated by semiconductor action
- The type of electronic switches are
- bipolar transistors, Power diode, MOSFET, etc.
RELAY
- A relay is an electrically operated switch.
- Relays are used where a circuit is controlled by a low power signal or where several circuits must be controlled by one signal.
- Sometimes the amount of electricity flowing in a device is so high that it is dangerous to humans.
- To protect people, relays can be put into a device to turn on and off special functions. the relay takes very little electricity to make it turn on and off a device with lots more electricity.
- It is used in motor control, electrical fuel pumps, industrial application, etc.
BATTERY
- Batteries convert chemical energy directly to electrical energy.
- The chemical reaction inside of the batteries separates positive charges from negative charges and puts one end of the battery cell.
- When a battery is supplying electric power, its positive terminal is the cathode and its negative terminal is the anode.
- Batteries and cells are power sources.
MOTOR
- An electrical machine that converts electrical energy into mechanical energy.
- It turns electrical energy into motion, usually rotation.
- The types of motors:
- AC Motor
- DC Motor
- The principle of working of a DC motor is that "whatever a current-carrying is placed in a magnetic field, it experiences a mechanical force"
AMPLIFIER
- An electronic device that can increase the power of a signal.
- Uses electric power to increase the amplitude of the signal.
- It has power to gain greater than one.
- Amplifiers are used in wireless communications and broadcasting, and in audio equipment.
RECTIFIER

- A rectifier is an electrical device that converts alternating current (AC) to (DC) is also called rectification.
- Rectifiers are used as components of power supplies and as detectors of radio signals.
TYPES OF RECTIFIER:
Half wave rectifier is a type of rectifier which converts the positive half cycle(positive current) of the input signal into pulsating DC (direct current) output signal.
A full-wave rectifier is a type of rectifier that converts both half cycles of the AC signal into pulsating DC signal.
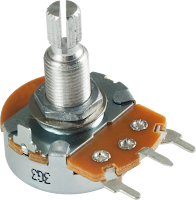
- Potentiometer are variable resistors.
- The potentiometer has 3 legs to create a voltage divider, which is basically two resistors in series.
- It is used for measuring electric potential and used to control electrical devices.
- Potentiometers are measured in ohms.
- Applications of potentiometer are audio control, television, motion control , etc.
INTEGRATED CIRCUIT(IC)
- Mass production capability, reliability and building-block approach to circuit design has ensured the rapid adoption of ICs in place of using discrete transistors.
- ICs are smaller, cheaper and faster.
- Ic's are used in computers, mobile phones, digital home appliances, etc













![[PDF] DOWNLOAD ALL PDF OF SIGNAL AND SYSTEM BY NAGOOR KONI, BP LATHI, SIMON HAYKIN, AND, ALAN V.OPPENEHEIM](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEgPCFP8yPgLYJAtQamfO6lIHHeavFDooTnC1wPOjh2hBiC5Zn63u104S_LNA1ynFt0t3HwWfmnMtoDNA84ZoYgZgNKL27ow2OCKRf99OuDoNpJtS46C4uAvImFXprjTcAG6eRmtFY1dV0c/w100/SIGNALS-and-SYSTEMS-LAB-VIVA-Questions-Answers.jpg)
![[PDF] DOWNLOAD ALL BOOK PDF OF ELECTROMAGNETICS BY MATTHEW NO SADIKU, HAYT AND BUCK, HASSAN SAEED](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEjAAhBHPPEFyx1J6hTLfmMGiv1ubgWp-P1Ou4sPrSmZQBQrp1UzyCqxggCXkFcQ9f9th7BrpSHuiKfHSjC3BEbZ2WnCVp0U1i4gL4pkq8ooQWPFf15UrOWjfhoy7hVSz6RC_kMgPm6f8JQ/w100/electromagnetics-medicine-618x371.jpg)
![[PDF] DOWNLOAD ALL BOOKS PDF FOR DIGITAL LOGIC AND DESIGN BY MORRIS MANO, THOMAS L.FLOYD, R.P JAIN, S SALIVAHANAN AND RONALD](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEioHfQtsPwXSOipfM6xdi-YZtNKUfJzdmyh1rKTBNM9KVJo8cvEBbylQ1iAx1wAoL3dW7ydIyQzTcC5scprqXVDuCWGRk1Izuxsx4ERRFYpoTOa5hrtO7Wvy4Kj5tiUxiOWaqN6p6r9D3c/w100/2285953_c5c2_2.jpg)
7 Comments
Thank You Very Much For Great Post. Dc Capacitor do not play an important role in DC circuits because it is impossible for a steady current to flow across a capacitor.
ReplyDeleteI appreciate your article. You truly share relevant and extraordinary knowledge. Thank you for keep sharing these valuable thoughts.
ReplyDeletehttps://supply.ctdi.com/shop/productdetail/2652/2000w-48vdc-rect
https://supply.ctdi.com/shop/productdetail/1518624/fbba
ReplyDeletehttps://supply.ctdi.com/shop/productdetail/1515790/fria-core
ReplyDeleteI appreciate your article. You truly share relevant and extraordinary knowledge. Thank you for keep sharing these valuable thoughts.
ReplyDeletehttps://supply.ctdi.com/shop/productdetail/1514723/radio
https://supply.ctdi.com/shop/productdetail/1516397/remote-radio-head
ReplyDeletehttps://supply.ctdi.com/shop/productdetail/1516247/frbg-rrh
ReplyDelete